Table of Contents
Medical billing is a critical component of any healthcare practice. It ensures that providers are reimbursed correctly for the services they deliver while maintaining compliance with healthcare regulations. Understanding the medical billing process is essential for clinics, hospitals, and healthcare administrators who want to optimize revenue cycles, reduce errors, and improve efficiency.
This guide provides a step-by-step overview of the medical billing process, detailing each stage, key responsibilities, and best practices to ensure accurate and timely payments.
What is the Medical Billing Process?
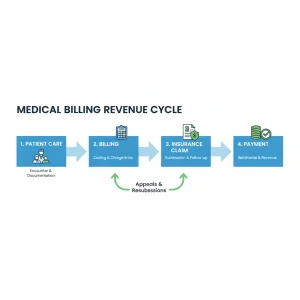
The medical billing process is a systematic series of steps that starts with patient registration and ends with reimbursement from insurance providers. It bridges the gap between patient care and financial management, ensuring healthcare providers receive timely payments for the services rendered.
The process is vital for:
- Accurate claim submissions
- Avoiding payment delays
- Reducing denied claims
- Maintaining regulatory compliance
Step 1: Patient Registration
Patient registration is the first step. Information collected includes:
- Personal details (name, DOB, address)
- Insurance information (policy number, provider)
- Primary care provider and referring physician
Accurate registration ensures that the claim process starts without errors. Mistakes here can lead to claim denials or delayed payments
Step 2: Insurance Verification
Before services are rendered, the insurance details must be verified:
- Coverage limits
- Co-pay amounts
- Pre-authorization requirements
- In-network vs out-of-network benefits
This step helps avoid denied claims and ensures patients are informed about out-of-pocket costs.
Step 3: Patient Encounter and Documentation
Every medical service provided must be properly documented. Accurate coding depends on detailed notes and records:
- Diagnosis codes (ICD-10)
- Procedure codes (CPT/HCPCS)
- Notes on tests, consultations, or procedures
Without proper documentation, claims can be rejected or underpaid.
Step 4: Medical Coding
Medical coders translate patient diagnoses and services into standardized codes. This allows insurance companies to process claims correctly.
Key points in coding:
- Use of accurate ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes
- Understanding payer-specific coding guidelines
- Avoiding undercoding or overcoding, which can cause legal issues
Step 5: Claim Creation
Once coding is complete, claims are generated. Claims include:
- Patient information
- Provider details
- Itemized list of services
- Codes and pricing
- Insurance information
Accurate claim creation is critical. Errors at this stage often lead to denials or delays.
Step 6: Claim Submission
Claims are submitted to insurance companies electronically or via paper. Most modern practices use Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) for faster processing.
Tips for claim submission:
- Double-check patient and provider details
- Verify codes and service dates
- Confirm payer requirements

Step 7: Payment Posting
Once the insurance company processes the claim, payments are posted in the practice’s billing system. This step includes:
- Posting insurance payments
- Recording patient co-pays
- Adjusting for deductibles or write-offs
Step 8: Handling Denials and Rejections
Not all claims are approved on the first submission. Common reasons for denials include:
- Incorrect coding
- Missing information
- Services not covered by insurance
A systematic denial management process ensures claims are corrected and resubmitted promptly, minimizing revenue loss.
Step 9: Patient Billing and Statements
After insurance processing, patients receive statements for remaining balances. Clear communication and accurate billing increase the likelihood of prompt payment.
Tips:
- Provide detailed, easy-to-understand statements
- Offer multiple payment options
- Send reminders for unpaid balances
Step 10: Reporting and Analysis
Reporting is the final stage in the medical billing process. Regular analysis helps practices:
- Monitor claim denial rates
- Track revenue cycle performance
- Identify bottlenecks
- Plan improvements in billing efficiency
Best Practices to Optimize the Medical Billing Process
- Implement electronic health records (EHR) and billing software
- Train staff on coding and claim submission
- Regularly audit claims and payments
- Maintain up-to-date insurance and regulatory knowledge
- Outsource to a medical billing company for complex claims
By following these steps, healthcare providers can reduce errors, accelerate reimbursements, and maintain compliance.