Medical Billing Compliance is one of the most critical responsibilities in healthcare administration. As regulations evolve and insurance rules become more complex, healthcare providers must stay updated with HIPAA, ICD-10, and federal billing guidelines to avoid costly penalties, denied claims, and legal risks.
This comprehensive guide explains what Medical Billing Compliance means, why it matters, and how healthcare organizations can stay compliant in today’s fast-changing regulatory environment.
What Is Medical Billing Compliance?
Medical Billing Compliance refers to the process of ensuring that all billing activities follow federal laws, HIPAA regulations, ICD-10 coding guidelines, payer policies, and ethical standards.
In simple terms:
Medical Billing Compliance ensures healthcare providers bill accurately, protect patient information, and follow legal requirements at every step.
Understanding HIPAA Compliance in Medical Billing
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) sets the national standards for patient privacy and protection. In Medical Billing Compliance, HIPAA plays a crucial role in maintaining confidentiality during the billing and coding process.
Key HIPAA Rules for Medical Billing Compliance
- Protecting Protected Health Information (PHI)
- Secure communication channels (encrypted emails, portals, EHR)
- Role-based access control within billing systems
- Staff training on HIPAA privacy and security policies
- Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with billing companies
Common HIPAA Violations in Billing
- Sharing PHI through unsecured emails
- Improper access by unauthorized staff
- Leaving printed medical bills in public areas
- Using outdated billing software with weak security
HIPAA violations can result in fines from $100 to $50,000 per incident — making Medical Billing Compliance essential.

Why ICD-10 Is So Important in Medical Billing Compliance
ICD-10 forms the backbone of accurate medical billing. Each code communicates the diagnosis and treatment details to the payer. Errors in ICD-10 coding directly impact revenue cycle performance.
How ICD-10 Supports Medical Billing Compliance
- Ensures claims are coded accurately
- Reduces claim denials
- Supports medical necessity documentation
- Helps maintain audit-ready records
- Aligns with payer-specific rules
Examples of ICD-10 Compliance Errors
- Upcoding: Using higher-paying codes without justification
- Undercoding: Leaving out necessary codes or using lower-level codes
- Unbundling: Billing services separately when a bundled code exists
Maintaining Medical Billing Compliance requires constant ICD-10 training, monitoring, and documentation accuracy.
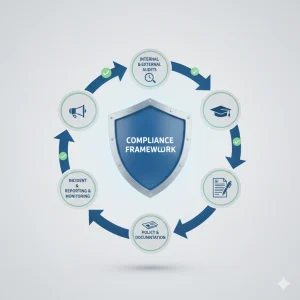
Essential Components of a Strong Medical Billing Compliance Program
An effective Medical Billing program protects providers from fraud, penalties, and claim denials.
Key Elements Include:
- Written compliance policies
- Regular audits and monitoring
- Ongoing ICD-10 and HIPAA training
- Internal billing quality checks
- Clear documentation standards
- Secure technology and access controls
The Risks of Non-Compliance in Medical Billing
Failing to follow Medical Billing can create serious consequences:
Financial Penalties
HIPAA fines and payer fines for fraudulent billing practices.
Legal Consequences
False Claims Act violations may lead to lawsuits.
Revenue Loss
Claim denials, delays, and reduced reimbursements.
Reputational Damage
Loss of patient trust and damaged provider reputation.
Operational Disruptions
Audits, investigations, and workflow interruptions.
Compliance is not optional — it's a critical safeguard.
How to Stay Updated with New HIPAA and ICD-10 Rules
1. Regular Staff Training
Frequent training keeps billing teams aware of new regulations.
2. Subscribe to CMS & AMA Updates
Official updates help maintain Medical Billing Compliance.
3. Use Advanced Billing Software
Automated alerts for ICD-10 changes reduce coding errors.
4. Conduct Internal Audits
Monthly and quarterly audits help catch compliance issues early.
5. Work With Certified Billing Specialists
Experts ensure adherence to HIPAA, CPT, and ICD-10 standards.
Keeping up with regulatory changes is the backbone of long-term Medical Billing Compliance.

Role of Technology in Medical Billing Compliance
Modern medical billing systems support compliance with:
- AI-powered claim scrubbing
- Real-time coding validation
- Automated HIPAA security features
- Predictive analytics for risk reduction
- Cloud-based encrypted storage
Technology enhances Medical Billing Compliance by minimizing human errors and strengthening documentation accuracy.
FAQs About Medical Billing Compliance
1. What is Medical Billing Compliance?
Short Answer: It ensures billing accuracy, HIPAA protection, and alignment with ICD-10 regulations.
2. Why is HIPAA important for medical billing?
HIPAA safeguards patient data and prevents privacy violations during billing processes.
3. How often should billing staff receive compliance training?
At least twice per year plus additional training when new rules are released.
4. What is the greatest risk of non-compliance?
Legal penalties and major financial losses due to claim denials.
5. How does ICD-10 affect Medical Billing Compliance?
ICD-10 ensures accurate coding and supports medical-necessity justification.
Medical Billing Compliance is essential for maintaining accurate claims, patient privacy, and legal protection. By following HIPAA guidelines, staying updated with ICD-10, implementing internal audits, and investing in secure technologies, healthcare providers can build a sustainable and compliant billing system.
Author Info
Author: Mangesh
Last Updated: November 2025
Category: Medical Billing & Compliance
Follow Us: facebook.com | instagram.com | linkedin.com | BackBoneDataSolutions.com